

And if the chemist says that she has a mole of atoms, she means that she has 6.022 x 10 23 atoms. And if the hardware store owner says she has a gross of bolts, she means that she has 144 bolts. When the club president arrives at the Tuesday morning officer's meeting and says I have a dozen donuts, she means that she has 12 donuts. In this sense, a mole is a counting unit much like the pair (2), the dozen (12), and the gross (144) are counting units.
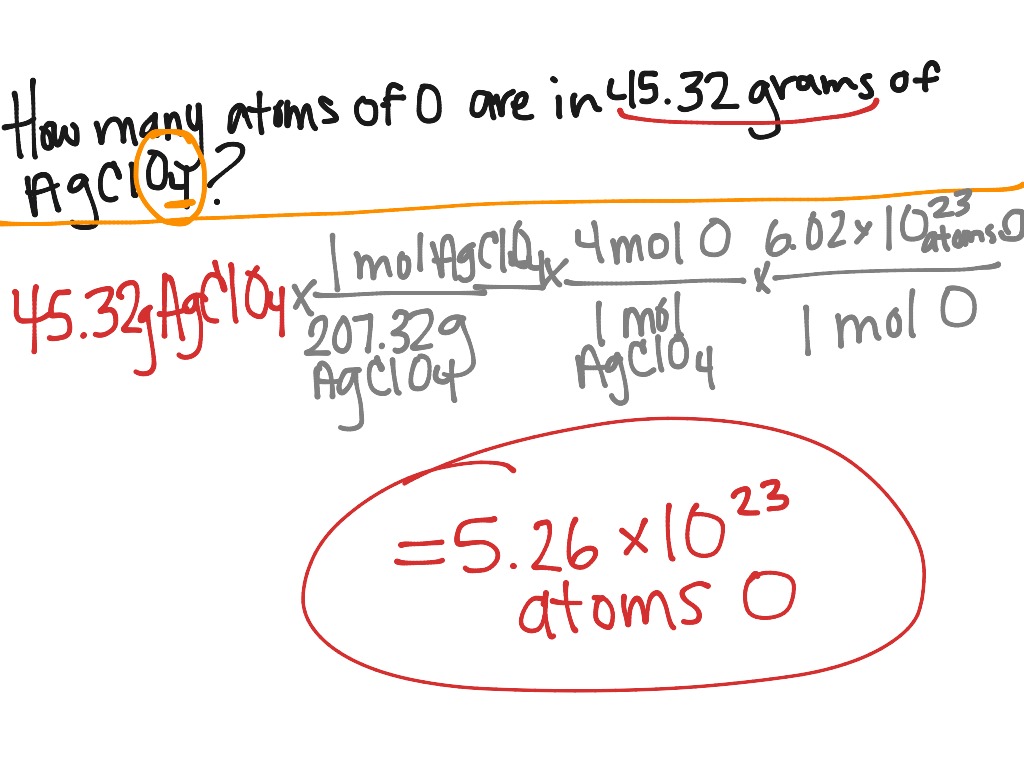
When there are this number of atoms in a sample, we say there is a mole of atoms. Avogadro's number is a number that has come to be known as 6.022 x 10 23. The super-sizing factor is known as Avogadro's number. While one could never isolate a single atom, let alone find a scale that is sensitive enough to measure its mass, it might be possible to have some super-sizing factor so that we could mass a large collection of atoms. So the concept of atomic mass and the atomic mass unit is a largely impractical concept when it comes to making a measurement. There is a need to somehow super-size this concept of an atomic mass. But atoms are very, very small and one could never isolate a single atom and measure its mass. PA 1, PA 2, and PA 3 represent the percent abundance of isotopes 1, 2, and 3.Ītomic mass values for the various isotopes allow a chemist to compare the mass of one atom relative to another atom. Where AM 1, AM 2, and AM 3 represent the atomic mass of isotopes 1, 2, and 3, and Atomic Mass = ( AM 1*PA 1 + AM 2*PA 2 + AM 3*PA 3 ) / 100 The average atomic mass of an element with three isotopes is calculated by the equation:Īve. The average atomic mass is the weighted average of the mass of the various isotopes of that element. Since a sample of an element like carbon is likely to have all three isotopes present, we commonly refer to the average atomic mass of carbon. Since the mass of an atom is largely dependent upon the number of protons and neutrons, the mass of an atom of any element depends upon the mass number of the specific isotope of that element.

The mass of all other isotopes can be determined experimentally using the assumption that Carbon-12 has a mass of exactly 12.000000 amu. The unit of mass is referred to as the atomic mass unit and abbreviated amu. This Carbon-12 isotope is the basis for the mass of all the other isotopes. So because chemists must start somewhere when determining the actual mass, it as decided to designate Carbon-12 to have a mass of exactly 12.00000 units. but not the actual mass of the atom itself.
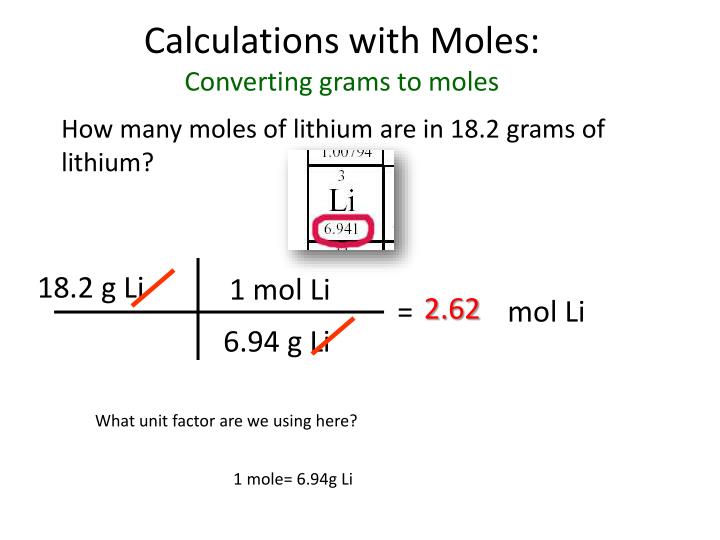
By experiment, we can determine the mass of one atom relative to another atom. These are all made-up numbers but you get the idea. Or we might determine that the mass of a Phosphorus-30 isotope is 1.499392 times greater than the mass of a Neon-20 isotope. Or we might determine the mass of a Magnesium-24 isotope to be 1.998972 times greater than the mass of a Carbon-12 isotope. For instance, we might determine Carbon-14 to be 1.166706 times greater than the mass of a Carbon-12 isotope. The word relative means that we can only determine the mass of a Carbon-14 isotope relative to the mass of a carbon-12 isotope. The point is that the relative atomic mass can be determined experimentally. The mass of a specific isotope relative to the mass of another isotope is easily determined using a mass spectrometer (but that's another topic all together). The periodic table lists the atomic masses of the various elements. The mass number is the sum of the atomic number (# of protons) and the number of neutrons. The numbers 12, 13, and 14 refer to the mass number of the three isotopes of carbon. Carbon has three such isotopes we refer to them as Carbon-12, Carbon-13, and Carbon-14. Atoms of the same element that have different number of neutrons are known as isotopes. But carbon atoms exist with 6 neutrons, 7 neutrons, and 8 neutrons. For instance, all atoms of carbon (C) have 6 protons. But the number of neutrons possessed by an atom of a given element can vary from atom to atom. This number is known as the atomic number. Percent composition calculations, empirical formula determinations, and average atomic mass calculations are also included in this set of problems. Problems range in difficulty from the very easy and straight-forward to the difficult and complex.Įach element of the Periodic Table has a unique number of protons. These problem sets focus on the use of Avogadro's number and molar mass values to convert between the number of particles in a sample, the moles in a sample, and the mass of the sample. There are 14 ready-to-use problem sets on the topic of Particles, Moles, and Grams. Particles-Moles-Grams: Problem Set Overview Problem Sets || Overview of Particles-Moles-Grams


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
